Empowering Cyber Defense: Automated Network security through XDR technology
Table of Contents
Network Security has never been more essential than it is in the contemporary digital age when cyber threats continue to become more sophisticated. The increasing number of linked gadgets, cloud-based services, and telecommuting put businesses up against several obstacles when it comes to protecting their infrastructure and confidential information from outside threats. Conventional security techniques are no longer enough to properly identify and prevent these attacks. This is where the idea of automated network security becomes revolutionary, supported by technologies that combine cyber security with Extended Detection and Response (XDR).
The Advancement of Network Security:
Since the days of basic firewalls and basic Antivirus Programs, Network Security has Advanced significantly. The security mechanisms put in place to protect against cyber-attacks have also evolved with time. But given how quickly threats have changed nowadays, the conventional approach to Network Security – which mostly depends on human intervention and reactive measures is no longer adequate. In addition, Automated Network Security services assist businesses in adhering to industry norms and regulations. Organizations must employ strong security measures to secure sensitive information to comply with several regulatory frameworks, including the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) and the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR). Businesses can prevent costly fines and reputational harm from non-compliance by automating security procedures and guaranteeing ongoing monitoring and compliance.
The Growth of Automated Network Security:
This marks an abrupt shift in the way businesses handle cybersecurity. Automated security solutions use automation, Machine Learning (ML), and Artificial Intelligence (AI) to identify and neutralize risks in real-time, as opposed to relying just on human analysts to do so. Organizations may reduce the risk of data breaches and cyber events and remain one step ahead of cyber attackers by adopting this proactive strategy. The expanding realization that human methods are insufficient for combating contemporary cyber threats is reflected in the rise of automated network security. Automated systems offer the information, scalability, and speed needed to successfully combat evolving cyber threats. The capacity of automated network security to constantly track network traffic and identify anomalies is one of its main advantages. These systems can detect unusual activity that might point to a possible security breach by utilizing machine learning and artificial intelligence. Automated security technologies may quickly identify and look into dangers such as strange data transmission patterns, illegal access attempts, or harmful software activities. This helps security teams keep one step ahead of hackers. The growth of Network security may lead to misunderstandings, and it can affect organizational security as well.
- Expanding Sophistication of Cyber threats: Conventional security measures are frequently ineffective in identifying and neutralizing cyber threats due to their increasing diversity and sophistication. Advanced technologies like Artificial Intelligence (AI), Machine Learning (ML), and Behavioral Analytics (BA) are used by automated network security solutions to constantly monitor traffic, identify anomalies, and react in real time to security incidents.
- Development of Network Complexity: It becomes impractical to monitor and administer networks manually as they get larger and more complex. Large volumes of data can be quickly analyzed by automated algorithms, which can also instantly spot possible security risks.
Why Network Security Automation:
Once network security services are virtualized, network security automation is an effective approach to streamline processes and enhance consistency and accuracy. Automation speeds up processes, lowers the possibility of human error, and refreshes entire virtual machine networks more quickly. In addition,
- Network security automation provides easy to use and scalable virtualization.
- Provides the largest decrease in total risk because you are improving the network’s basic (or infrastructure) layer.
- Saves the cost by avoiding the need to purchase improvements to your hardware.
- Conserve the time with zero touch network operation and efficiency.
- Acquire more advanced control of information.
- Enforces good security practices by automating network policy validation and enforcement processes and enables repeatable procedures.
Examples of Network security automation:
| Firewall Rule Management | Automated Firewall Rules | Security rules can be created and modified automatically in response to application needs, intelligence on threats and network traffic statistics. |
| Rule Optimization | To improve productivity and protection, automation tools examination the current firewall rules, spot redundancies, and optimize them. | |
| Intrusion Detection and Prevention System (IDS/IPS) | Automated Alerts and Actions | Depending on the threat level, IDS/IPS systems automatically identify suspicious activity, issue alerts, and carry out predetermined actions (such as blocking an IP address) |
| Signature Updates | IDS/IPS signatures are kept current by automation, guarding against known attack vectors and weaknesses. | |
| Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) | Log gathering and Correlation | To detect possible security problems, SIEM tool gathers logs from a variety of network devices, connect events, and analyze data. Efficiency in handling the massive volume of logs is aided by automation. |
| Automated Incident Response | SIEM systems could launch automated reactions in response to security incidents. These responses may include banning IP addresses, alert security professionals, or starting additional investigation. | |
| Network Access Control (NAC) | Autonomous Network Access Regulations | NAC programs impose access restrictions according to user role, the condition of devices, and their geographic location. Automation makes sure that before allowing a device to enter the network, it complies with security regulations. |
| Guest Network Provisioning | NAC can automatically allocate visitors who connect to a network to a separate guest network with restricted access. | |
| Vulnerability Management | Automated Scanning | To find flaws in servers, network devices, and the application, frequency scheduled scans are conducted automatically. |
| Patch Management | To shorten the window exposure, automation technologies are used to prioritize and apply security fixes and susceptible systems. | |
| Network Segmentation | Automatic Micro Segmentation | Micro segmentation separates applications and workloads in contemporary networks. Automation technologies use workload factors to dynamically define and implement segmentation policies. |
| Certified Management | Automatic Certificate Renewal | SSL/TLS Certificates expire occasionally. |
| Certificate Development | Automation provision and distribution upon the completeness of new services. |
Understanding XDR Cybersecurity:
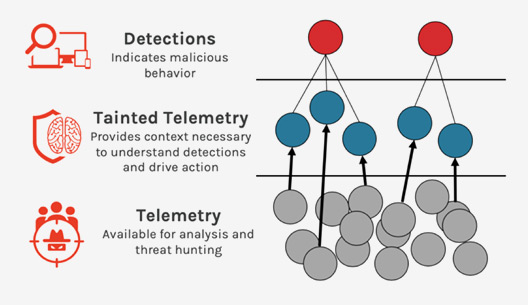
A next generation security solution named Extended Detection and Response (XDR) correlates and incorporates data from an array of Security tools and sources across the IT architecture of an enterprise. XDR offers comprehensive knowledge of possible threats across endpoints, network, cloud environment and apps, in contrast to typical security technologies that operate in silos. Through the centralization and analysis of this data on a strengthened platform, XDR facilitates more efficient threat detection, investigation, and response for companies. We have teamed up with industry experts Cybereason and CrowdStrike to offer the finest protection available for any kind of device from mobile to cloud.
Key Components of XDR Cybersecurity:
- Data Collection and Correlation: Real time security telemetry data is collected by XDR systems from logs, networks, endpoints, and other sources. Following that, this data is evaluated and connected to find movements, anomalies, and security hazards.
- Using machine learning and Artificial Intelligence: To evaluate enormous amounts of data and spot novel risks, XDR makes use of machine learning and AI technologies. These algorithms can recognize evidence of compromise, hostile activity, and suspicious behavior that conventional security technologies might ignore.
- Automated Response: XDR’s potential to automate threat mitigation procedures based on defined playbooks and policies is one of its primary features. To stop further damage, this involves quarantining suspicious files, halting malicious traffic, and isolating contaminated endpoints.
- Orchestration and Interactions: Using APIs and defined protocols, XDR systems enable smooth interaction with current security products and infrastructure. This makes it possible for enterprises to expedite incident response procedures and coordinate security operations across many platforms.
Strengths of XDR powered Automated Network Security
- Detecting threats in Real Time: Through the continuous monitoring and analysis of security monitoring data, XDR helps enterprises to quickly identify possible attacks and take appropriate actions to prevent any harm.
- Enhanced Control and Visibility: XDR offers enterprises a thorough understanding of their IT Infrastructure, enabling them to proactively spot security holes and vulnerabilities. Organizations can manage their security posture and compliance more efficiently due to this increased visibility.
- Decreased Alert Fatigue: By decreasing false positives and alert restlessness, automated network security with XDR lightens the workload on security specialists. Organizations may direct their resources towards resolving real security threats and hazards by automating threat identification and response procedures.
- Flexibility and Scalability: XDR Solutions can grow with organizations as their needs shift, whether they are branching out into new markets, adopting new technologies, or developing new infrastructure. Due to its scalability, automated network security can adapt to emerging threats while maintaining its effectiveness over time.
- Proactive Threat Hunting: By utilizing threat information and complex analytics, XDR empowers enterprises to hunt out threats in a proactive manner. Organizations may proactively avoid breaches of information and cyber events by recognizing and conducting research into possible risks before they get more serious.
Conclusion
In the current cyber environment, automated network security using XDR technology is a very effective defense tactic. Organizations may proactively protect their network against the future of Cybersecurity by utilizing XDR, which allows for the seamless integration of advanced threat detection, response, and investigation capabilities. XDR technologies provide unmatched visibility and control through automated incident response, anomaly detection, and continuous monitoring, allowing security teams to quickly discover and address security threats. Furthermore, by utilizing penetration testing techniques, XDR improves efficacy by verifying security controls and spotting possible weaknesses before bad actors can take advantage of them. Using a comprehensive security approach, automated network security with XDR technology gives businesses the flexibility and resilience they need to defend against increasingly complex cyberattacks. The future of Cybersecurity centers around automated network protection with XDR cybersecurity, which helps enterprises identify, address, and eliminate attacks with greater effectiveness in the ever-changing threat landscape of today. Using cutting-edge technologies like Artificial Intelligence (AI), Machine Learning (ML), and automation, XDR enables enterprises to defeat Cybercriminals and defend their infrastructure and sensitive data from constantly shifting threats. Automated network security with XDR will become more and more important as businesses embrace digital transformation and technologies to protect themselves from cyber threats and maintain continuous operations.